accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests|acetabular labrum diagnosis : import All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular . Resultado da 🔴 Ao Vivo 10/12/23 | Santo Terço de Aparecida com o Padre Antonio Maria | Terço de Aparecida hoje. Evangelização. 11.1K subscribers. Subscribed. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 2024 © The Pirate Filmes.com.br - Baixar Filmes Torrent, 4k, BluRay 1080p 720p, Filmes via Torrent, Download Filmes via Torrent, Filmes Dublados e .
acetabular labrum diagnosis
Magnetic resonance arthrography as a diagnostic test for acetabular labral tears has been shown to demonstrate 66%-71% sensitivity and 44%-75% specificity. The accuracy of intra-articular injection of anesthetic to determine an intra . A more recent study in those with acetabular labral tear has shown that conservative management over the course of 1 year with corticosteroid injection, activity .
All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular .
accessories for permeability tester
In a recent study evaluating diagnosis of longstanding groin pain, the most prevalent condition was hip joint pathology, with acute labral tears and impingement syndromes accounting for a . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally . 3.0 T MRI is more recommended to detect acetabular labral tears than MR Arthrography: an updated meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. Peng Zhang, Chunbao Li, . Acetabular labral tears may occur because of abnormal bony morphology (femoroacetabular impingement or secondary proximal femoral deformity), dysplasia, capsular .
For MRI (eight studies), the pooled sensitivity for detecting acetabular labral tears was 66% (95% CI 59 to 73) and pooled specificity was 79% (95% CI 67 to 91). For MRA (15 studies), the . Labral tears in the hip are now becoming widely recognised as a source of anterior hip/groin pain and intra-articular pathology. The prevalence of acetabular labral tears in some .
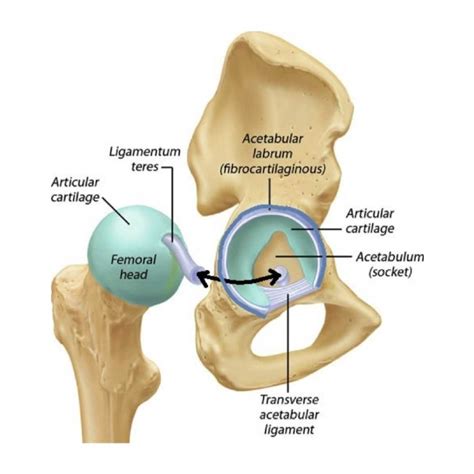
Using arthroscopy as the reference standard, hip labral tears were clinically suspected with 80-85% accuracy. The clinical diagnostic accuracy of the PT, OS, and ORs was high with no significant difference between examiners. In this study, an experienced PT, an OS, and two ORs demonstrated similarly .The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure which lines the acetabular rim of the hip joint. The joint is surrounded by ligaments that work to keep this articulation intact. Movements of this joint are facilitated by the articulation of .
Conventional MRI was assessed in 13 studies and MRA was assessed in 16 studies. Whilst both MRI (0.5-3T) and MRA (0.5-3T) presented with a moderate sensitivity and specificity (sensitivity 66%, 87%; specificity 79%, 64%), diagnostic accuracy of MRA appeared to be superior to MRI in detecting acetabular labral tears on ROC curve interpretation. All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests. Although a positive McCarthy test is not very common in labral lesions, it has a high specificity.Hip labral tears commonly occur between 8 to 72 years of age and on average during the fourth decade of life; Women are more likely to suffer than men; 22-55% of patients with hip or groin pain symptoms are found to have an acetabular labral tear; Up to 74.1% of hip labral tears cannot be attributed to a specific event or causeThis review concluded that both magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA) may be useful adjuncts in the diagnosis of hip acetabular labral tears in adults, although MRA appeared superior to conventional MRI. Given the limitations of the evidence available and the analysis undertaken, these conclusions should be treated with .
The Fitzgerald test utilises two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. Technique [edit | edit source] . The validity and accuracy of clinical diagnostic tests used to detect labral pathology of the hip: a systematic review. Manual therapy. 2011 Aug 1;16(4):318-26.Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22–55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. An ALT can lead to biomechanical deficiencies and a loss of stability to the coxafemoral joint due to the labrum serving as a stabilising structure of this .
Depending on the cause and extent of the tear, the surgeon might remove the torn piece of labrum or repair the torn tissue by sewing it back together. Complications of surgery can include infection, bleeding, nerve injury and recurrent symptoms if the repair doesn't heal properly. A return to sports usually takes 3-6 months.
Posterior labrum tear: This tear occurs at the back of the shoulder joint. SLAP tear: A superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tear occurs at the top of the glenoid (shoulder socket) and extends from the front to the back, where the biceps tendon connects to the shoulder. This is a common injury for athletes such as baseball pitchers and .
Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for the diagnosis of hip femoroacetabular impingement/labral tear: a systematic review with meta-analysis Br J Sports Med . 2015 Jun;49(12):811. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2014-094302. A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or .Over time, this can result in tears of the labrum and the breakdown of articular cartilage (osteoarthritis). Types of FAI. There are three types of FAI: Pincer. This type of impingement occurs because extra bone extends out over the normal rim of the acetabulum. The labrum can be crushed under the prominent rim of the acetabulum. Cam.acetabular labral tears. Once considered an uncom-mon entity, labral tears as a source of symptoms and functional limitation in the hip region have become more recognized. A labral tear was arthroscopically identified in 90% of individuals with mechanical hip symptoms.29,55 However, isolated labral tears occur in
Interpretation The impingement test is helpful in identifying acetabular labral tears. If this test is negative and if a labral tear is still suspected, ultrasound can reliably diagnose most tears of the acetabular labrum. . and accuracy of MR arthrographic findings compared to those of hip arthroscopy (Chan et al. 2005, Freedman et al. 2006, .Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22-55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. . clinical examination and special test findings that are unique to the condition. Imaging methods such as MRI, CT and .Hip Labral Tear Tests. Specific clinical tests are used to check for labral tears and understand the potential location of the tear (tears in front vs tears at the back). Three common hip labral tear tests performed in a clinic or doctor’s .
So far, several studies have assessed sonographic examination for diagnosis of acetabular labral tears, but the validation of this test has been inconsistent [34–41]. Sonographic examination has a lesser diagnostic ability than CTA or MRI/MRA; thus, it is of limited use in clinical practice [34, 35, 41]. CTA is another diagnostic method for .acetabular labral tears. Once considered an uncom-mon entity, labral tears as a source of symptoms and functional limitation in the hip region have become more recognized. A labral tear was arthroscopically identified in 90% of individuals with mechanical hip symptoms.29,55 However, isolated labral tears occur in
Arthroscopic surgery is regarded as the gold standard for diagnosing acetabular labral tear and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is a sensitive imaging technique to evaluate the acetabular labrum other than bony abnormalities and cartilage changes. 4 Most people, however, would use an MR arthrogram to diagnose acetabular labral tears. Chopra et al. 5 evaluated 68 . Acetabular labral tears are an area of increasing interest to clinicians involved in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal complaints of the hip. This review systematically evaluated the evidence for the diagnostic accuracy and validity of reported symptoms, physical examination and imaging in this complex population. Studies published in English prior to May 2010 were .
management of acetabular labral tears is lacking [4, 10, 11]. With the advent of new arthroscopic techniques, focus on treatment of acetabular labral tears has most commonly featured arthroscopic labral repair or debridement [3, 4]. Despite the growing body of evidence for surgical treat-ment, there is still an incomplete understanding as to opti-Wang WG, Yue DB, Zhang NF, et al. Clinical diagnosis and arthroscopic treatment of acetabular labral tears. Orthop Surg 2011;3:28–34. Beaule PE, O’Neill M, Rakhra K. Acetabular labral tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91:701–10. Martin RL, Enseki KR, Draovitch P, et al. Acetabular labral tears of the hip: examination and diagnostic challenges.
Figure 4-1 Classifications of acetabular labral tears: radial flap, radial fibrillated, and peripheral longitudinal. (Adapted from Lage LA, Patel JV, Villar RN. The acetabular labral tear: an arthroscopic classification. Arthroscopy. 1996;12:269-272.) The primary risk factors identified for acetabular labral tears are anatomic variants that affect hip joint function and .
The acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that is triangular in cross-section and attaches to the bony rim of the acetabulum [1–4].The labrum is approximately 2 to 3 mm thick and is wider and thinner anteriorly, and thicker posteriorly [4–7].By providing up to a 21% increase in acetabular depth, the labrum enhances hip joint stability and increases .The acetabular labrum is a ring of protective cartilage. It lines the rim of your hip socket (acetabulum). Your acetabular labrum holds your thigh bone securely in the joint, which allows flexibility and motion. It also cushions your joint and evenly distributes pressure during physical activity. . Hip Labral Tear Tests for Diagnosis. Acetabular labral tear, as the name implies, is a tear involving the acetabular labrum of the hip. . most accurate imaging study (91% vs 36% on native MRI) minimally invasive compared with arthroscopy. highly diluted intra-articular Gd-injection (0.0025 mmol/ml) with joint distension (10-20 ml) allows optimal assessment of the labrum on T1 .
cement permeability tester
webExplore the map and shoot the enemy team. Pick up weapons along the way. There are various weapons you’ll find, from the default AK47 to a grenade launcher, rocket .
accuracy of acetabular labrum tear tests|acetabular labrum diagnosis